As your application grows or when the requirements change, you may need to add a new column to an existing table. By default, when using an SQL database, a new column will be added at the end of the existing columns. However, you might prefer to have them in a specific order. This can be easily accomplished using a Laravel migration.
In this tutorial, we will walk you through the process of adding a new column, specifically a publisher column, after the publish_date column in a table called books. By following the steps outlined below, you’ll be able to effectively manage the order of your table columns.
Let’s get started!
Step 1: Create a Migration
To begin, open your terminal and navigate to your Laravel project directory. Then, execute the following Artisan command to generate a migration file:
php artisan make:migration add_publisher_column_to_books --table=booksThe command used above generates a new migration file in the folder /database/migrations. Since we provided a --table=books parameter, it will conveniently autofill our table name in the migration file’s schema.

artisan make:migration to Create a MigrationStep 2: Edit the Migration File
Locate and open the generated migration file in the database/migrations directory. Inside the up method we’ll use the Schema facade to add the new column. Here we’ll use the method ->after() to position the it after the publish_date column.
To do this use the following code:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class AddPublisherColumnToBooks extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::table('books', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->string('publisher')->after('publish_date');
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::table('books', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->dropColumn('publisher');
});
}
}Save the changes made to the migration file and return to your terminal.
Step 3: Run the Migration
Now, execute the following command to run the migration to add the publisher column at the desired position:
php artisan migrateIt should output the following:

artisan migrateWhen we look at our table, before and after running the migration, we can see that it has achieved the desired result:
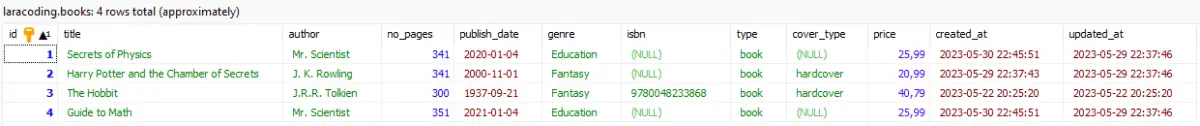
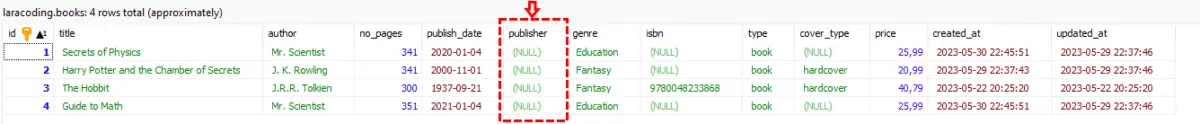
Adding Multiple Columns After A Specific Column
Note that we can also write the migration to add several columns in our preferred position.
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class AddPublisherColumnToBooks extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::table('books', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->string('publisher')->nullable()->after('publish_date');
$table->string('edition')->nullable()->after('publisher');
$table->string('language')->nullable()->after('edition');
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::table('books', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->dropColumn('publisher');
$table->dropColumn('edition');
$table->dropColumn('language');
});
}
}Note that Laravel 8.27 and newer allow for a shorter syntax, in which we only need one call to ->after() while specifying multiple columns. Therefore, we can use the following code to achieve the same result:
// ...
public function up(): void
{
Schema::table('books', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->after('publish_date', function ($table) {
$table->string('publisher')->nullable();
$table->string('edition')->nullable();
$table->string('language')->nullable();
});
});
}
// ...Conclusion
By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can easily add a new column after a specific column in your SQL table using Laravel migrations.
In our example, we demonstrated how to add a “publisher” column after the “publish_date” column in the “books” table. We also looked at an example of adding multiple columns while maintaining our preferred order.
Using this knowledge you’ll have more control over the order of your columns in your own applications. Happy coding!

